Late talkers
Absolute indications for immediate evaluation of language delay
- No babbling, pointing, or gesturing by 12 months
- No single words by 16 months
- No two-word spontaneous phrases by 24 months
- Any regression in language or social skills at any age
15-25% of young children have some type of communication disorder
- Incidence of SLI (specific language impairment) in 5 y. old was estimated to be 7,6%
National Institutes of Health – USA (a condition also called language-learning
impairment, developmental dysphasia, developmental language disorder or dev.
aphasia)
- Late talkers - most 67% to 84% are boys
- if a child has SLI, there is a 25% chance that another family member will be affected
- Dysarthria, verbal apraxia, phonological disorder
- Suttering – fluency disorders
- Cleft palate
Auditory-phonological processing presents the heterogenity of specific language impairment (SLI): identification of speech sounds appears to be a problem, more typical SLI – where language comprehension is impaired, but the most obvious problems are with expressive syntax and phonology, problems with semantic and association function, disorder of the short-term memory, auditory processing deficit – inability to recognize the key words, inability to use intrinsic- extrinsic redundancies to complete speech sound.
Treatment of SLI children in our department
- All children underwent detailed phoniatric examination
- analysis of speech and language functions audiometric tests,discriminative auditory tests,
- test of phonological awareness
- test of word repetition/ short-term memory
- central dichotic tests
- study of auditory evoked potentials
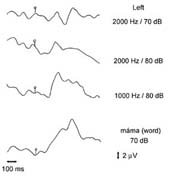 |
 |
 |
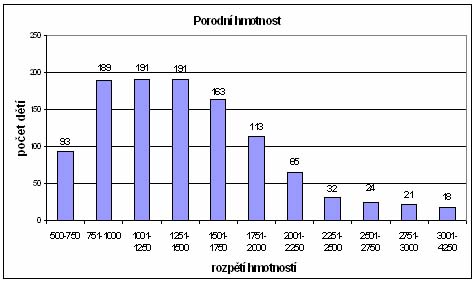
Hearing screening in high risk infants
(results of 1100 children)
- The results of 10 years study
- Using TEOAE and ABR
- Very low birth weight under 1500 g
- The predominant factor is gestational age
- The most specific risk is a low birth weight
- Results: 27 children with hearing loss
- 2,45% of incidence
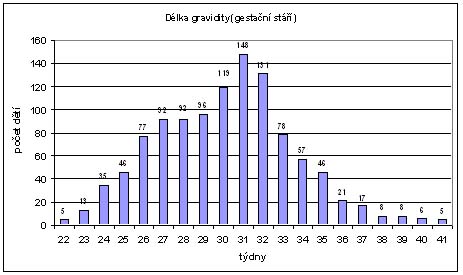 |
 |
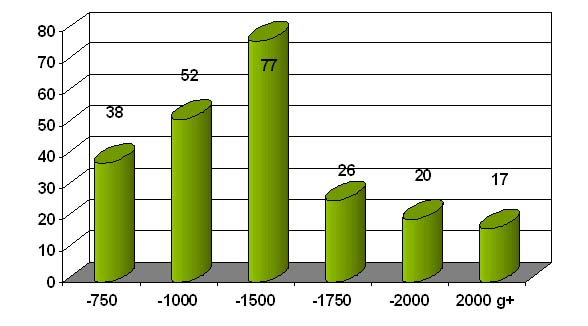
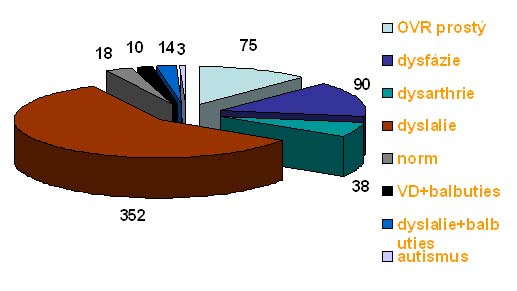
Speech and language screening
in high risk infants
- 600 risk children especially with low birth weight
- Results: 40% children with speech and language disorder
- Late talker:
SLI children, dysarthria, stuttering, dyspraxia, dyslexia, dysgraphia
and combination…
Fluency disorders
- Stuttering
- Neurogenic disfluency
- stroke, head trauma, dementia, tumors, drug usage
- extrapyramidal diseases
- Psychogenic disfluency
- Spasmodic dysphonia (spastic)
- Tourette syndrome
- Linguistic disfluency
- Normal developmental disfluency
Stuttering
Onset characteristics – two stages (Bluemel)
Primary stuttering
- Easy, intermittent repetitions of the first word or syllable in a sentence
Secondary stuttering – progression
- Clonic types – more rapid, tense behaviors involving muscle tension, interrupted breathing and facial tension
- Tonic types
Stuttering - fluency disorder
- Stuttering varies by time, situation, and language factors
Special conditions that immediately eliminate stuttering: choral reading – with a speaker who is fluent, lipped speech, whispered speech, prolonged speech with or without Delayed Auditory Feedback, rhytmic speech, shadowing, singing, slowed speech
- Etiology – multifactorial, as the interaction of predisposing factors, negative emotional response, the incomplete cerebral dominance Tudory, consequences of a subcortical lesion
- Therapy – treatment, family based treatment, speech treatment – relationship to age (school-age, adolescents, adults), psychotherapy, relaxation….
Cleft lip and palate
Cleft palate disorders
- Birth defect (prevalence 1/500-600) – a lack of continuity of structure of some of various segments which normally combine to form the upper lip and palate (the roof of the mouth) – those structures are deficient
- ¼ cleft lip only, ½ cleft lip and palate, ¼ cleft palate
- In any event there is an open passageway connecting the mouth cavity and the nose
- Velopharyngeal incompetence
- Feeding problems, respiratory infections,
- Dental and occlusal problems
- Cleft palate – communication problems: hearing impairment – conductive, middle ear disease, language development - may be slower in the beginning of to talk, speech-sound articulation and voice quality problems
- Velopharyngeal incompetence and its effects on speech: inability to close the velopharyngeal port
- Palatolalia, palatophonia – hyperrhinophonia